Why Congress Can Impeach Obama
Peter H. Schuck / New York Times
22 نوفمبر 2014
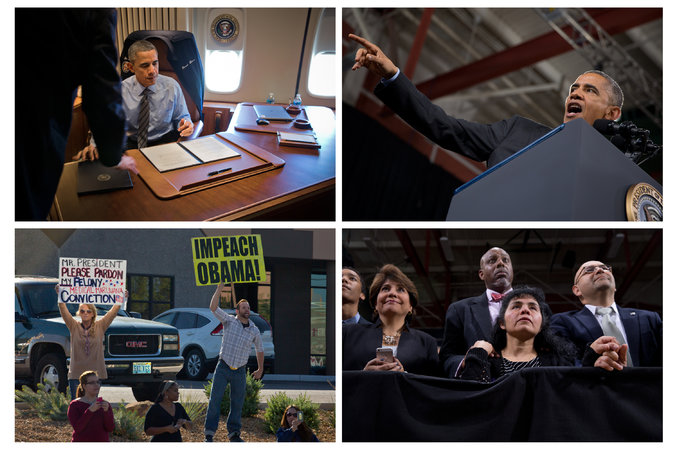

NOW that President Obama has granted legal relief to as many as five million undocumented immigrants, Republicans are thrashing about for an effective response. Only a few hard-liners are talking about impeachment now, but more could join them out of frustration with their other options.
Many people in both parties have tried to quell such talk by saying the president is within his powers to issue the order. The problem is, the pro-impeachment Republicans are right: There is a plausible case for taking that step.
By constitutional design, impeachment for “treason, bribery, or other high crimes and misdemeanors” is a political accusation and initiates a political remedy, not a legal one. It is pretty much up to Congress to define and apply “high crimes and misdemeanors,” and no court would second-guess it. The next Congress could find that the president had violated his oath to “faithfully execute” the laws by refusing to enforce important provisions of the Affordable Care Act, No Child Left Behind and, now, the Immigration and Nationality Act.
The president surely has some power to withhold prosecution, but granting legal status and work permits to millions of people most likely exceeds his discretion. No judge can decide the precise scope of his discretion because no one, including Congress, has legal standing to challenge his order in court.
Of course, many lawyers at the Justice Department and elsewhere disagree, noting that prosecutorial discretion is pervasive, that there isn’t enough money to prosecute all violators, that the president will continue to prosecute criminals and illegal border crossers, and that earlier presidents have done the same thing. These are serious arguments. But as an immigration and administrative law teacher who strongly favors more legal immigration and even broader legislative relief than Mr. Obama’s order grants (and who voted for him twice), I find them unconvincing.
In the Immigration and Nationality Act, Congress carefully limited prosecutorial discretion by allowing the president to waive exclusions and deportations only under narrowly defined conditions. The act also granted the president broad power to suspend the entry of “any class of aliens” he finds detrimental to the national interest — but, significantly, did not give him corresponding authority to legalize “any class” of undocumented people he thinks deserve it.
President Obama has cited several cases of suspended enforcement as precedent. But in those cases, Congress had authorized the immigrants in question to apply for green cards; the president merely suspended enforcement against their closest family members until they, too, could get their own cards.
Most telling, Mr. Obama, a former constitutional law professor, once rejected the very arguments he now embraces. Last year he said that extending amnesty beyond the so-called Dreamers (the children of undocumented immigrants brought here at an early age) would be “ignoring the law in a way that I think would be very difficult to defend legally.” It is hard to think of a confession more damning to his position in a court of law, in a congressional court of impeachment and in the court of public opinion.
Still, does his overreaching constitute an “impeachable offense” under the constitutional standard? History suggests that it might. In the early 1800s, two federal judges were impeached for far less: noncriminal intoxication, indecency, bias and other judicial improprieties.
True, the standard for impeaching presidents should be more demanding than for judges. Even so, in 1868 President Andrew Johnson was impeached by a deeply partisan, Radical Republican-dominated House. Johnson — a conservative Democrat who rose from the vice presidency when Abraham Lincoln, a Republican, was assassinated — was impeached mainly for firing a cabinet member (which he almost certainly had the legal right to do), but also for obstructing policies that Congress enacted. (Impeachment proceedings against Richard M. Nixon and Bill Clinton involved criminal conduct more egregious than Mr. Obama’s policy unilateralism.)
But even if Congress has constitutional authority to impeach the president, that doesn’t mean it should. Quarrels between a president and Congress over the statutory limits on his authority are common, and the precise boundaries can be hard to discern. However truculent Mr. Obama’s defiance may be on this issue, Congress has other ways to stymie it — for example, barring the action by statute. Such tactics are within the normal give-and-take of interbranch disputes. Americans, including many like me who want a legislative amnesty, would support Congress’s use of them here.
Impeachment, moreover, would tend to normalize its use as a political weapon, even though the framers intended that it be used only in extreme cases that endanger the republic. Only inveterate Obama haters think that is true here.
The new Congress would accomplish nothing of consequence despite urgent national needs and voters’ demands for cooperation. This would deepen the public’s growing disgust with our government, a disgust that, properly directed, can spur needed reform, but if taken too far erodes the government’s capacity to do what only government can and must do. Perhaps most dangerous, impeachment of an already lame-duck president would further disable him for the next two years from defending American security and interests in a remorselessly turbulent, perilous world. All Americans should fervently pray that it doesn’t come to that.
 عن أمل جنبلاط المتجدد: لبنان يستحق النضال
عن أمل جنبلاط المتجدد: لبنان يستحق النضال
 صحافيون أم عرّافون!
صحافيون أم عرّافون!
 ماذا يجري داخل أروقة بيت الكتائب المركزي؟
ماذا يجري داخل أروقة بيت الكتائب المركزي؟


 عن الخرائط التي تُرسم والإتفاقات التي تتساقط!
عن الخرائط التي تُرسم والإتفاقات التي تتساقط!
 “الإنحراف في الحياة”/ بقلم كمال جنبلاط
“الإنحراف في الحياة”/ بقلم كمال جنبلاط
 هاشتاغ #صار_الوقت يحل أولاً في حلقة جنبلاط
هاشتاغ #صار_الوقت يحل أولاً في حلقة جنبلاط
 طاولة نقاش عن أزمة الصحافة في جامعة AUST
طاولة نقاش عن أزمة الصحافة في جامعة AUST
 عبدالله: ليظهر لنا وزير مكافحة الفساد حرصه في صفقات البواخر والفيول
عبدالله: ليظهر لنا وزير مكافحة الفساد حرصه في صفقات البواخر والفيول
 عبدالله: غريب أمر وزارة مكافحة الفساد!
عبدالله: غريب أمر وزارة مكافحة الفساد!

 Comment to Uri Avnery: How Sad What Is Looming Ahead
Comment to Uri Avnery: How Sad What Is Looming Ahead
 “Not Enough!”
“Not Enough!”
 … لمن لم يقرأ يوسف البعيني/ بقلم وسام شيّا
… لمن لم يقرأ يوسف البعيني/ بقلم وسام شيّا
 كمال جنبلاط في مولده الأول بعد المائة: تعاليمه وأفكاره ما زالت الحلّ/بقلم عزيز المتني
كمال جنبلاط في مولده الأول بعد المائة: تعاليمه وأفكاره ما زالت الحلّ/بقلم عزيز المتني
 رئيس حزب/ وليس (… سابقاً)/ بقلم د. خليل احمد خليل
رئيس حزب/ وليس (… سابقاً)/ بقلم د. خليل احمد خليل
 التوازن السياسي في لبنان
التوازن السياسي في لبنان
 لبنان… مشاريع انقلابية مؤجلة
لبنان… مشاريع انقلابية مؤجلة
 جنبلاط وحَمَلة أختام الكاوتشوك
جنبلاط وحَمَلة أختام الكاوتشوك
 Le Liban est un symbole de tolérance
Le Liban est un symbole de tolérance
 Our Automated Future
Our Automated Future
 The True Origins of ISIS
The True Origins of ISIS
 Les Misérables vs. Macron
Les Misérables vs. Macron
 عذراً أيها المعلم/ بقلم مهج شعبان
عذراً أيها المعلم/ بقلم مهج شعبان
 رساله الى المعلم / بقلم ابو عاصم
رساله الى المعلم / بقلم ابو عاصم
 إلى روح القائد والمعلم كمال جنبلاط/ بقلم أنور الدبيسي
إلى روح القائد والمعلم كمال جنبلاط/ بقلم أنور الدبيسي
 أسرار وعناوين الصحف ليوم الجمعة 14 كانون الاول 2018
أسرار وعناوين الصحف ليوم الجمعة 14 كانون الاول 2018